Arm Bones Vector Medical Content

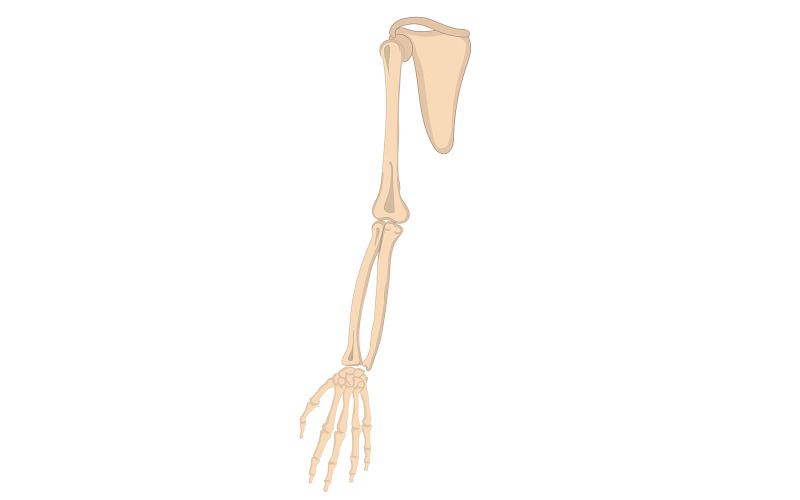
The arm is composed of several bones that provide structure, and support, and enable movement. These bones are divided into the upper arm, forearm, and hand.
Upper Arm:
- Humerus:
- The single bone in the upper arm.
- Extends from the shoulder to the elbow.
- Connects with the scapula (shoulder blade) at the shoulder joint and the radius and ulna at the elbow joint.
Forearm:
- Radius:
- One of the two bones in the forearm.
- Located on the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm.
- Connects to the humerus at the elbow and to the carpal bones at the wrist.
- Ulna:
- The second bone of the forearm.
- Located on the medial (pinky) side of the forearm.
- Connects to the humerus at the elbow and to the carpal bones at the wrist.
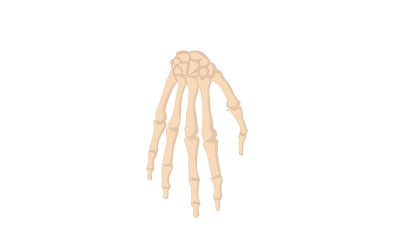
Hand:
- Carpal Bones:
- Eight small bones are arranged in two rows at the wrist.
- Allow for the flexibility and movement of the wrist.
- Metacarpal Bones:
- Five long bones in the palm.
- Connect the carpal bones to the phalanges.
- Phalanges:
- Fourteen bones that make up the fingers.
- Each finger has three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal), except the thumb, which has two (proximal and distal).
Key Joints:
- Shoulder Joint: Formed by the humerus and scapula, allows for a wide range of arm movements.
- Elbow Joint: A hinge joint formed by the humerus, radius, and ulna, enabling bending and extending of the forearm.
- Wrist Joint: Formed by the radius and carpal bones, allowing for the wrist's flexion, extension, and rotational movements.
These bones work together to provide strength, flexibility, and dexterity to the arm, enabling a wide range of movements necessary for daily activities.
0 Reviews for this product
0 Comments for this product